Introduction
Quiz is an important Interactive method of teaching and learning, which gives an opportunity to students for active student-centered learning 1. It is feasible to adopt interactive teaching in a conventional curriculum inspite of all the challenges like large batches and need to allocate additional teaching hours. Clinical images and tests are considered useful tools to enhance the memorization of facts and information in medical education 2. Thus, we need to find unique ways of making learning active and interesting 3. A study shows students were favorably inclined to the Quiz sessions which can thus be used as an effective teaching learning tool 4. The students find the Quiz method to be an interesting and useful learning tool 5. Aside from content retention, formative assessment through quizzes can benefit both learners and teachers in a number of ways 6. The purpose of introducing Quiz as a teaching learning method in our study is to increase interactivity between students and teachers and among the students themselves. The aim of increasing interactivity is to provide faculty with information on what, how much, and how well students are learning. Such interactivity inspires the students to be self- directed and life- long learners. Quiz nurtures team and competitive spirit. Implementing such interactive techniques requires leadership, team building skills and overcoming logistic barriers. Active teaching strategies are designed to make the learning process more interactive and interesting. Various studies done show most students are favorably inclined to the quiz sessions suggesting its utility as an interactive and effective study tool. Rapid scoring provides immediate and explanatory performance feedback to the students.
Introduction of interactivity using Quiz as teaching method in Anatomy to 1st year undergraduate medical students and perceive its effectiveness and impact on learning of the students. To improve interpersonal interaction and relationships and team-based learning among the students and also to motivate the faculty to train in conducting interactive quizzes at various levels.
Materials & Methods
Informed consent was taken from the students and faculty before conducting the Quiz.
The study was conducted in the department of Anatomy in CMCH, Ludhiana, Punjab.
Clearance was taken from Institutional Research Board and Ethical Committee
Sensitization session on interaction and Quiz was conducted for the students and faculty
Interactivity via Quiz session was introduced on completion of Abdomen-pelvis and Head-Neck regions of Anatomy.
The questions for the Quiz were prepared by all the faculty. The questions included Multiple choice questions, Brief answer questions, Picture based questions, Case based questions and Rapid fire.
Students were asked questions on the completed region in an interactive manner by the Quiz master.
The class was divided randomly into 4 groups of 18-19 students each- Group A, B, C and D.
Each group chose a spokesperson. Answers given by this spokesperson only were accepted.
The students in one group could discuss and interact amongst themselves and give a common answer to the spokesperson. But the students of one group could not discuss or interact with students of other groups.
There was specific time given to each group for the common discussion.
Time was managed by a faculty as time keeper by ringing a bell.
Rounds of question (each round containing 4 questions each were conducted
Each round began with one group and if the group were not able to answer, the question was passed to the next group.
Marks were allotted by one of the faculty on the board for each round.
In the end correct answers were discussed by the Quiz master. During this activity the Quiz master and the students discussed why the correct option was chosen and why the other options were incorrect. There was a two-way interaction between the students and the Quiz master.
After that students and faculty’s feedback was taken after each session by a validated questionnaire.
The questionnaires consisted of perceptions and feedback on Quiz session by the students and faculty.
Students’ feedback:
-
A feedback form was given to students containing ten questions based on Likert scale and 2 open-ended questions.
-
Students were asked to tick any one response based on their perception at that moment about recently interactive quiz and give suggestions in the open-ended questions
Faculty feedback:
-
A similar form was given to faculty which contained ten questions on Likert scale and two open-ended questions.
-
Faculty was asked to tick any one response based on their perception at that moment about recently used Interactive quiz technique and give suggestions in the open-ended questions.
Observations & Results
Qualitative results of the study
Perception of students and faculty towards quiz method was assessed by a structured pre-validated feedback form, the results of which are given below:
Feedback from students
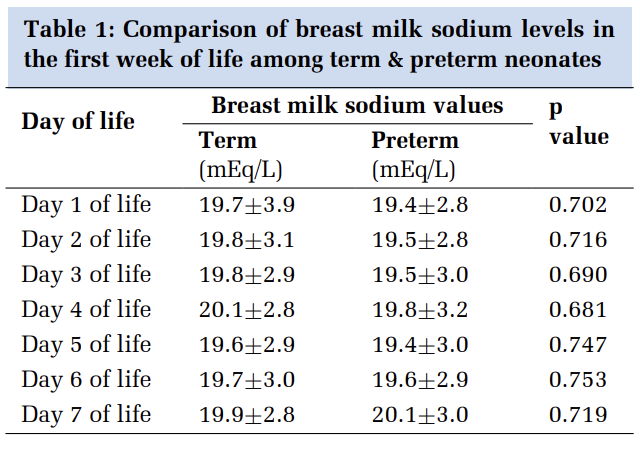
A Feedback of the students was taken after conducting Quiz on each session. The data obtained from feedback form is tabulated in Figure 1 .
The given figure shows the perceptions of students on the Quiz session. It is evident that in each response the majority of students are in agreement. 65% students felt that the use of these techniques will enhance their performance during examinations.

Feedback from faculty
A Similar feedback also taken from the faculty was after each Quiz session. The data obtained from feedback form is tabulated in Figure 2.
The given figure shows the perceptions of faculty after the Quiz session was conducted.
Table 1 is obtained by clubbing the positive and negative responses together. Responses more than 80% have been highlighted. 93% students felt that they are looking forward to the use of more Quizzes. 84.5% of the students felt that use of these techniques will affect their exam performance positively. 93% students felt other subject teachers should also use these techniques

|
S No |
Questions |
Agree + Strongly agree |
Neither agree or disagree |
Disagree + Strongly Disagree |
|
1 |
Quiz is more interactive as method of teaching- learning compared to a long lecture. |
64 (91.5) |
3 (4.2) |
2 (2.8) |
|
2 |
Interaction during the Quiz has increased my attention in the session |
66 (93.0) |
2 (2.8) |
2 (2.8) |
|
3 |
Interacting during the Quiz motivated me to read more about the topic. |
61 (85.9) |
6 (8.5) |
3 (4.2) |
|
4 |
It helped me to understand the topic better. |
60 (84.5) |
6 (8.5) |
4 (5.6) |
|
5 |
It has helped me in better retention of the topic. |
60 (84.5) |
6 (8.5) |
4 (5.6) |
|
6 |
It helped me in correlating Anatomy with clinical case. |
58 (81.7) |
6 (8.5) |
6 (8.5) |
|
7 |
It made me understand the importance of learning Anatomy. |
58 (81.7) |
9 (12.7) |
3 (4.2) |
|
8 |
Quiz gave me an opportunity to interact with the faculty. |
56 (78.9) |
9 (12.7) |
4 (5.6) |
|
9 |
Quiz gave me an opportunity to interact with my fellow students. |
57 (80.3) |
11 (15.5) |
2 (2.8) |
|
10 |
Interaction during Quiz gave me a chance to practice team learning. |
56 (78.9) |
13 (18.3) |
1 (1.4) |
|
11 |
Interactive Quiz should be conducted for all the regions of Anatomy. |
67 (94.4) |
1 (1.4) |
2 (2.8) |
|
12 |
Quiz should be incorporated as an interactive teaching Method along with regular lectures in other Basic Science subjects for under graduates. |
66 (93.0) |
3 (4.2) |
1 (1.4) |
DA-C = Strongly Disagree + Disagree, N = No change/can’t say, A-C = Agree + strongly agree
Table 2 is obtained by clubbing the positive and negative responses together. Responses more than 60% have been highlighted.100% of teaching faculty believe that Quiz increases interactivity among students and between students and teachers. 80% felt Quiz motivates students to study more and also helped in better retention of the topics. 80% felt use of this technique should be done by other basic science subjects also.
|
S No |
Questions |
Agree + Strongly agree |
Neither agree or disagree |
Disagree + Strongly Disagree |
|
1 |
Quiz is more interactive as method of teaching- learning compared to a long lecture. |
4 (80.0) |
1 (20.0) |
0 (0) |
|
2 |
Interaction during the Quiz has increased my attention in the session |
5 (100.0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
3 |
Interacting during the Quiz motivated me to read more about the topic. |
5 (100.0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
4 |
It helped me to understand the topic better. |
5 (100.0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
5 |
It has helped me in better retention of the topic. |
4 (80.0) |
1 (20.0) |
0 (0) |
|
6 |
It helped me in correlating Anatomy with clinical case. |
4 (80.0) |
1 (20.0) |
0 (0) |
|
7 |
It made me understand the importance of learning Anatomy. |
4 (80.0) |
1 (20.0) |
0 (0) |
|
8 |
Quiz gave me an opportunity to interact with the faculty. |
4 (80.0) |
1 (20.0) |
0 (0) |
|
9 |
Quiz gave me an opportunity to interact with my fellow students. |
5 (100.0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
10 |
Interaction during Quiz gave me a chance to practice team learning. |
4 (80.0) |
1 (20.0) |
0 (0) |
|
11 |
Interactive Quiz should be conducted for all the regions of Anatomy. |
5 (80.0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
12 |
Quiz should be incorporated as an interactive teaching Method along with regular lectures in other Basic Science subjects for under graduates. |
4 (80.0) |
1 (20.0) |
0 (0) |
DA-C = Strongly Disagree + Disagree, N = No change/can’t say, A-C = Agree + strongly agree
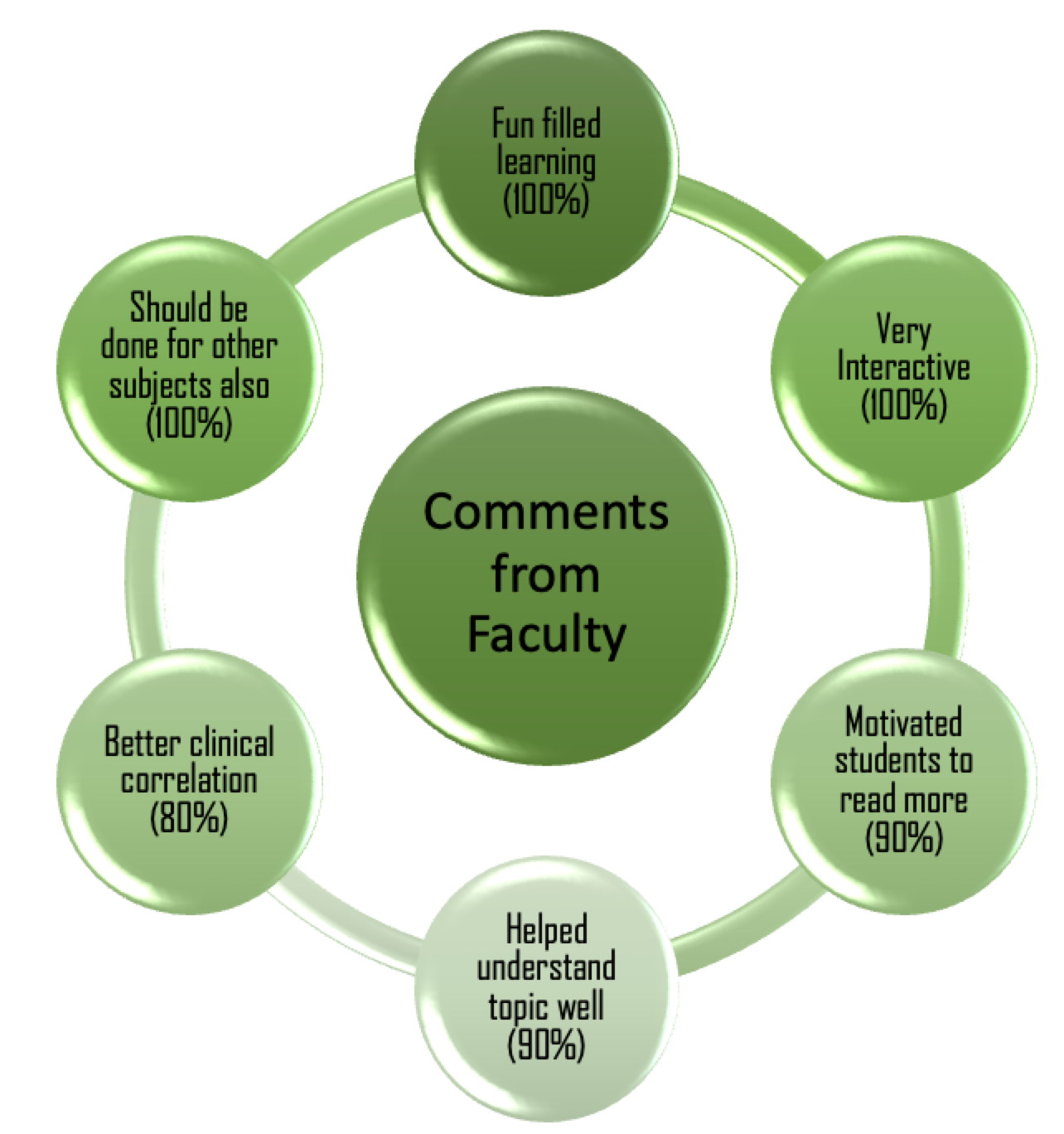
Figure 3, Figure 4 show the responses stated by students and faculty respectively. Majority of students and faculty feel that the quiz method of learning is fun filled, interactive, motivated the students to read more, helps better understanding of the topic, helps in better correlation with the clinical part and it should be conducted for all regions of Anatomy.

Discussion
In the present study conducted in the department of Anatomy, Cmch, we wanted to assess perception of students towards Quiz as an interactive and fun filled method of teaching and learning in the first-year undergraduate medical students. By using Quiz method, we wanted to increase interest and awareness in learning Anatomy which is otherwise considered a dry subject.
As per the feedback received:
Quiz method was a fun filled method of learning which broke the monotony of listening to one sided didactic lecture. It developed interest in the topic, kept the students fully involved and increased knowledge about the topic. This finding was consistent with the other study conducted by Thomas and Melor 7. Another study by Vanesa et al 8 also supports this notion.
Learning and understanding Anatomy is very essential for the students in the first year itself as they are able to correlate it better clinically later. The Quiz conducted by us had many questions on case-based scenarios and clinical aspects. And therefore, students had a positive response that the Quiz method will help them achieve the above target. Similar findings were observed in a study done by Jennifer Hillman 9.
In this study we conducted Quiz on 2 regions of Anatomy. The students opined that Quiz should be conducted for all the regions of Anatomy and also for all the subjects studied in basic sciences. This opinion of the students is supported by Valeh and Mostafa 10 where in the students really liked this method as it involved participation of the whole class, motivated them to study more, was interactive and interesting and very different from the routine lecture classes.
In routine classes each and every student cannot get individual attention. It is also difficult for the students to concentrate continuously for long spans of time in a lecture. So, we can instead use Quiz to teach even the difficult topics in an interactive and an interesting manner. This will also develop more motivation in the student in learning Anatomy and other basic sciences subjects. Studying and discussing in small groups is more advantageous than long classroom lectures. New methods like evidence-based learning, problem-based learning are also being introduced based on the above said concept. But among these also Quiz is highly interactive, interesting and a fun filled method of learning. Using group discussions successfully for teaching and learning in preclinical years have already been reported by Rotti SB et al 11.
By using Quiz students got an opportunity to gain deep insight in the subject of Anatomy as they referred other books, research articles and used internet for the preparation. It also enabled them to apply their knowledge critically. Most of all it built a healthy competitive spirit among the teams. This method ensured greater interaction and participation of the students in teaching and learning process.
Undergraduate medical curriculum should consider incorporation of interactivity enhancing and effective learning tool like Quiz for better learning and performance of the students.
Interactive Quiz can be beneficial for both faculty and the students.
Benefits to Faculty: - It helps faculty to focus on student learning. Faculty gets trained to conduct interactive Quizzes at all levels. Team building and better interpersonal relationships are formed.
Benefits to Students: - Students may be hesitant to ask questions during class. Interacting in a Quiz give students opportunities to provide anonymous feedback to their instructor about their learning. During these interactive and fun filled sessions, students may become more involved in their learning when they find other students taking interest in answering questions. Through greater involvement, students are likely to become more self-directed learners, and may be more motivated during the course.
Using such tools to increase interactivity during learning sessions will have multiple benefits in learning and motivation by the students as compared to conventional lecture teaching that can become boring and monotonous and will also help the faculty to analyze and restructure their teaching methods and interests.
Here I would like to suggest some strategies that can be implemented while conducting an interactive Quiz:
First thing is to create a space big enough for all the competitors, the host and the audience like large hall or a classroom. An area can be set up where competitors face each other preferably with tables and buzzers.
For the quiz to be effective we can keep it short and simple with a concrete goal in mind. It is better to include mix question types that have easy answer choices. These questions can be asked in a fun and interesting manner. Assigning weights to the questions and providing feedback is an important step towards increasing the quiz centered learning.
Last but not the least, choosing and promoting the winner will create a competitive spirit in the students that can drive them to learn more.
Conclusion
The use of interaction increasing method like Quiz in classroom teaching has been taken positively by faculty and students. Majority of students and faculty are enthusiastic about continuing to use it later also. This method should be used by teachers in other departments also. Majority of students also stated that they feel their exam performance will also be increased by the use of this method.
Recommendation
It is recommended that Quiz method should be included in teaching all regions in Anatomy and also in teaching other subjects of the basic sciences to make subjects more interactive and interesting.
Further research can also be conducted to discover newer and better ways to make the quiz more interesting and interactive. Studies can be done to use newer technologies available today to improve the standard of the quiz prepared.
Infact interactive quizzes can be conducted not only at classroom levels but also interclass and intercollege level and their effectiveness on the learning of the students can be studied.